Imagine this: A customer’s frustration mounts as they wait days for a response to their urgent support request. Meanwhile, your team is unsure of who’s responsible or what the promised turnaround time actually is. Seems familiar?
That’s where Service Level Agreements (SLAs) come into play. Think of customer service SLAs as the golden handshake between your business and its customers, clearly defining what level of service they can expect and when they can expect it.
In this guide, we will understand everything about customer service SLAs—from major types to key components. We will also explore a few ready-made SLA templates to help you get a better idea.
Let’s get started!
What Is an SLA Template?
An SLA (Service Level Agreement) template is a structured document that defines the services a provider will deliver, the quality standards, and the penalties for not meeting them. It’s like a formal agreement to ensure everyone’s on the same page about what’s expected.

Image Source: Legal Templates
For instance, imagine a cloud storage provider offering 99.9% uptime in their SLA. This means your data would be inaccessible for only about 43.8 minutes per month. If the provider exceeds that downtime, the SLA might specify compensation like a percentage refund of the subscription fee, service credits, or even complete refunds, depending on the severity and duration of the outage.
What Are the Types of Customer Service SLAs?
Here are some of the most common types of customer service SLAs:
1. Response Time SLA
A response time SLA outlines the maximum duration a company has to acknowledge or respond to a customer’s inquiry or issue after receiving it. It ensures customers feel heard promptly, enhancing trust and satisfaction.
Example: A support team promises to respond to all high-priority tickets within two hours, medium-priority tickets within 12 hours, and low-priority tickets within 24 hours.
Use Case: This is particularly important for industries like IT services or e-commerce, where customers expect quick acknowledgment and feel confident their concerns are being addressed.
2. Resolution Time SLA
A resolution time SLA defines the time frame within which customer problems must be resolved completely. It ensures the service provider prioritizes efficiency and allocates resources effectively to meet customer expectations.
Example: A telecommunications provider commits to resolving internet outages within four hours for urban areas and within 24 hours for rural areas.
Use Case: This is common in industries like technology, telecommunications, and utilities, where downtime or unresolved issues can severely impact the customer experience and operations.
3. First Call Resolution SLA
This SLA measures the percentage of customer issues resolved during the initial interaction without requiring follow-ups or escalations. It emphasizes providing accurate and comprehensive solutions promptly.
Example: A call center guarantees that 85% of customer inquiries will be fully resolved on the first call, minimizing the need for callbacks.
Use Case: Ideal for call centers, customer support desks, and technical support teams focusing on efficiency and customer satisfaction by reducing repeated interactions.
4. Uptime/Availability SLA
An uptime SLA commits to ensuring a specific level of service availability, minimizing downtime that could disrupt customer operations or experiences. It is a critical metric for reliability.
Example: A cloud service provider guarantees 99.9% uptime, meaning downtime will not exceed 8.76 hours per year, with a refund policy for breaches.
Use Case: This is vital for SaaS, cloud hosting, and online platforms, where uninterrupted service is crucial for customers to maintain their operations and revenue streams.
5. Wait Time SLA
A wait time SLA sets maximum allowable delays for customers waiting for service, such as on a call, in a queue, or for live chat. It helps improve the overall customer experience by minimizing frustration.
Example: A contact center promises an average call wait time of less than three minutes, with peak times not exceeding five minutes.
Use Case: Often used in customer service departments, contact centers, and retail environments where long wait times can negatively affect customer satisfaction and brand perception.
6. Escalation SLA
This SLA establishes clear guidelines for when and how unresolved customer issues are elevated to higher levels of support or management, ensuring critical problems are addressed promptly.
Example: If a technical issue remains unresolved for more than eight business hours, it will automatically escalate to a senior technician and then to a manager after 24 hours.
Use Case: Useful in organizations with tiered support structures, such as IT service desks or complex B2B environments, to ensure persistent issues receive proper attention.
7. Customer Satisfaction SLA
A customer satisfaction SLA focuses on maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction, typically measured through tools like surveys, Customer Satisfaction Scores (CSAT), or Net Promoter Scores (NPS).
Example: A company commits to achieving a minimum CSAT score of 90%, monitored through quarterly surveys, and addressed if satisfaction dips below the target.
Use Case: Especially relevant for customer-centric industries like hospitality, retail, and healthcare, where customer feedback directly influences reputation and business success.
8. Custom SLAs
Custom SLAs are tailored agreements designed to meet the unique needs of specific clients or industries. They allow for flexibility and customization to align with the client’s goals and expectations.
Example: A B2B software vendor offers a dedicated account manager, monthly performance reviews, and guaranteed 24/7 premium support for enterprise clients.
Use Case: This is often seen in high-value or strategic customer relationships, such as enterprise-level contracts, where standard SLAs do not sufficiently address the complexities of the partnership.
What Are the Key Components of Customer Service SLAs?
The key components of a customer service SLA include:
1. Scope of Service
This component specifies the range of services covered under the SLA, detailing what the provider will deliver and what falls outside the agreement’s boundaries.
It ensures clarity about the exact nature of the services offered, preventing misunderstandings and managing customer expectations effectively.
2. Performance Standards
Performance metrics are at the heart of an SLA, defining measurable standards like response time, resolution time, and uptime requirements.
For instance, it might guarantee acknowledgment of customer issues within 24 hours and resolution within five business days. These standards provide a benchmark for assessing service quality and accountability.
3. Roles and Responsibilities
Both the service provider and the customer have distinct roles and duties outlined in the SLA.
This section ensures that each party understands their responsibilities, such as providing timely information, adhering to escalation procedures, and ensuring proactive communication to facilitate smooth service delivery.
4. Support Framework
This section outlines how customers can access support, including the channels available (e.g., email, phone, chat) and the service operation hours.
Whether support is 24/7 or restricted to business hours, these details set clear expectations about how and when assistance can be sought.
5. Prioritization and Escalation
Issues may vary in criticality, and this component defines the priority levels (e.g., low, medium, high, or critical) and the expected response and resolution times for each.
It also describes the escalation process, ensuring that unresolved issues are addressed by higher management within a defined timeframe.
6. Monitoring and Reporting
To ensure transparency, this section explains how service performance will be monitored, measured, and reported.
Regular performance reports detailing adherence to SLA commitments allow both parties to evaluate the agreement’s effectiveness and address any deviations promptly.
7. Remedies and Exclusions
SLAs include provisions for remedies, such as financial penalties or service credits, if the service provider fails to meet agreed standards.
They also define exclusions where service lapses may not be covered, such as issues arising from force majeure events or customer negligence, providing a fair framework for accountability.
8. Review, Revision, and Termination
Finally, the SLA must remain adaptable to changing needs. This component establishes a review schedule to reassess the agreement’s relevance and effectiveness and includes conditions for amendments or termination.
It also outlines dispute resolution and termination procedures in case of persistent non-compliance or evolving business needs.
5 Ready-to-Use Customer Service SLA Templates
Here are five commonly used types of customer service level agreement templates, along with examples:
1. Response Time Customer Service SLA
It focuses on how quickly customer service responds to inquiries or complaints. It typically defines response times based on the urgency or priority of issues.
Use Case: Suitable for businesses providing technical or customer support where quick acknowledgment is critical.
Response Time SLA Template:
- Purpose: To define response time commitments for customer support.
- Scope: Applies to all support channels (email, chat, phone, etc.).
| Priority Level | Description | Response Time |
|---|---|---|
| Low | General inquiries | Within 48 business hours |
| Medium | Non-urgent technical issues | Within 24 business hours |
| High | System malfunction impacting users | Within 4 business hours |
| Critical | System outage or business-critical impact | Within 1 hour |
- Exclusions: Delays caused by factors outside the provider’s control.
- Review Cycle: Monthly performance audits.
- Escalation Process: Issues not resolved within SLA timelines will be escalated to the senior management team.
2. Resolution Time Customer Service SLA
It sets expectations for the time it will take to resolve issues after they are acknowledged.
Use Case: Ideal for service providers offering repair, troubleshooting, or technical services.
Resolution Time SLA Template:
- Purpose: Ensure timely issue resolution to minimize customer impact.
- Scope: Covers incidents reported by customers.
| Priority Level | Description | Resolution Time |
|---|---|---|
| Low | Cosmetic issues or minor queries | Within 7 business days |
| Medium | Functional issues with workarounds | Within 3 business days |
| High | Service disruption for a single user | Within 1 business day |
| Critical | Widespread outage or major defect | Within 4 hours |
- Dependencies: Customer must provide all relevant details promptly.
- Penalties: 10% service credit for each missed SLA target.
- Amendments: SLA terms are subject to annual review.
3. Uptime Customer Service SLA
It guarantees a certain percentage of service availability, ensuring systems remain operational.
Use Case: Suitable for SaaS companies, IT infrastructure providers, and any business relying on continuous uptime.
Uptime SLA Template:
- Purpose: To ensure system reliability and availability for customers.
- Scope: Covers the availability of the primary service platform.
| Metric | Target |
|---|---|
| Uptime Percentage | 99.9% monthly uptime guarantee |
| Downtime Exceptions | Scheduled maintenance (max 2 hours/month) |
- Monitoring Tools: System logs, monitoring software.
- Incident Reporting: Downtime incidents must be reported within 24 hours for compensation eligibility.
- Compensation: For uptime below 99.9%, a 10% monthly service credit applies.
4. Quality of Service Customer Service SLA
It specifies quality metrics for service interactions, such as customer satisfaction (CSAT), Net Promoter Score (NPS), and adherence to quality standards.
Use Case: Best for companies prioritizing high-quality customer interactions, e.g., call centers, consulting firms.
Quality of Service SLA Template:
- Purpose: Ensure consistently high-quality customer service.
- Scope: Covers all customer-facing interactions.
| Metric | Target |
|---|---|
| CSAT | 90% positive feedback score |
| NPS | 50 or higher |
| Call Resolution Rate | 85% resolved on the first contact |
| Response Quality | 95% compliance with company guidelines |
- Reporting: Monthly performance dashboards.
- Training: Quarterly training programs for service representatives.
- Penalties: Failure to meet metrics will result in internal reviews and customer compensation (if applicable).
5. Volume-Based Customer Service SLA
It sets expectations based on the volume of requests a customer can make within a specified period, e.g., tickets per month or hours of service.
Use Case: Common in managed services and B2B contracts, where usage limits are defined.
Volume-Based SLA Template:
- Purpose: Manage customer expectations regarding service volume.
- Scope: Covers all service requests within contractual limits.
| Service Type | Volume Limit (per month) | Additional Costs |
|---|---|---|
| Technical Support | 20 support tickets | $50 per additional ticket |
| Consultation Hours | 10 hours | $100 per additional hour |
| Software Updates | 2 major updates | Not applicable |
- Carry-Over Policy: Unused volume cannot be carried over to subsequent months.
- Reporting: Usage reports are provided quarterly.
- Renewal Terms: SLA limits are reviewed annually during contract renewal.
These service level agreement samples can be modified according to the business needs.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
Customer Service SLA Best Practices You Should Follow
Here are some customer service SLA best practices you should follow to enhance customer satisfaction and operational efficiency:
1. Set Clear Expectations
Your SLA is like the rulebook for your service commitments, so it must be very clear. Define response times, resolution times, and scope of services in detail. Ambiguity leads to unmet expectations, so outline exactly what customers can expect and what’s outside your boundaries.
2. Involve Stakeholders in SLA Creation
A one-size-fits-all SLA rarely works. Get input from customers, your support team, and leadership when drafting SLAs. This ensures that expectations align with customer needs and internal capabilities, preventing unrealistic promises or overlooked gaps.
3. Regularly Review & Update SLAs
Customer needs and business capabilities evolve, and so should your SLA. Schedule periodic reviews to adjust timelines, add new service offerings, or refine metrics. Stale SLAs are as good as no SLAs.
4. Use Measurable Metrics
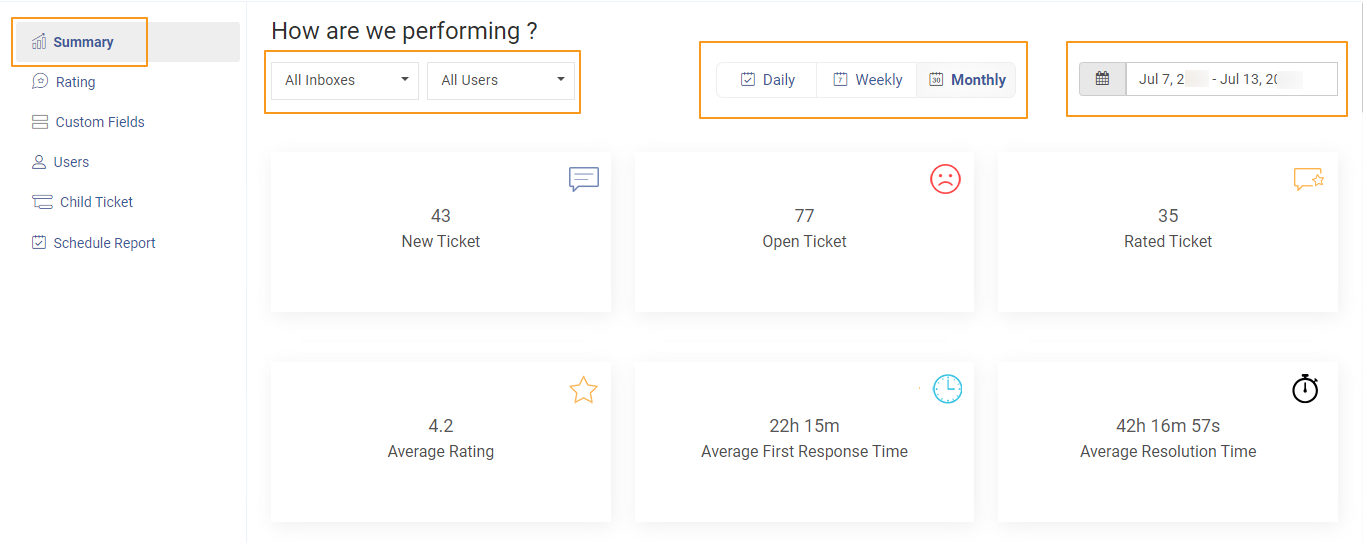
Trackable help desk metrics like “First Response Time” and “Resolution Time” are essential. Avoid vague language like “as soon as possible.” Clear metrics make accountability straightforward and help you spot areas for improvement.
5. Communicate Proactively
When service issues arise, don’t leave customers guessing. Proactively communicate delays, updated timelines, or escalations. Keeping them in the loop builds trust, even when things don’t go as planned.
6. Empower Teams to Meet SLAs
Equip your support teams with the tools, training, and authority they need to resolve issues efficiently. If your SLAs require a 24-hour resolution, ensure staff has the resources to make that happen without unnecessary escalations or delays.
Elevate Your Support With SLA-Driven Customer Service
Customer Service SLAs aren’t just agreements; they’re the backbone of exceptional customer experiences. SLAs help your team set clear expectations, measure performance and hold teams accountable so that customers feel valued and supported.
Remember that a proactive SLA strategy can reduce response times, improve resolution rates, and build lasting customer trust.
But setting SLAs is one thing, and measuring them is another. To truly achieve this, you need the right help desk software like ProProfs Desk, which streamlines SLA management with features like automated ticket prioritization, time tracking, and performance reporting. These capabilities empower your team to meet targets and deliver top-notch customer service consistently.
FREE. All Features. FOREVER!
Try our Forever FREE account with all premium features!
 We'd love your feedback!
We'd love your feedback! Thanks for your feedback!
Thanks for your feedback!