If you handle a customer service team, you know life at the office is nothing short of a battlefield. One second, there is an email complaint shared by an existing customer; the next, there is an inquiry by a prospect demanding urgent attention.
A powerful support ticketing system can help you turn this chaos into a streamline process.
So if you have any questions about what a help desk ticketing system is, its functionality, or its benefits, this guide will share all the answers you need.
Let’s start with the basics.
What Is a Ticketing System?
A ticketing system is a software application used to manage and track support requests and customer inquiries. It provides a centralized platform for customers or users to submit support requests and for support teams to manage and resolve them.
The system provides tools for support teams to categorize, prioritize, assign, and resolve tickets. Some ticketing systems also include automated notifications, knowledge management, and analytics to help support teams work more efficiently and effectively.
In summary, a ticketing system is a valuable tool for organizations to manage customer support and ensure timely and efficient resolution of customer inquiries.
What Are the Key Features of a Robust Ticketing System for Customer Support?
A ticketing system facilitates the management and resolution of customer inquiries, issues, and requests. Some notable features include:
1. Automated Ticket Assignments
By leveraging predefined rules or algorithms, automated ticket assignments efficiently route incoming tickets to the most suitable agents or teams.
This process optimizes workflow distribution, ensures equitable task allocation, and promotes timely resolution by matching the expertise and availability of agents with the nature of the issue.
2. Canned Responses
Canned responses are pre-written templates or snippets of text designed to address frequently encountered customer inquiries or issues.
They expedite communication by allowing agents to quickly select and customize relevant responses, ensuring consistency in messaging, reducing response times, and enhancing overall efficiency in customer support interactions.
3. Parent-Child Ticketing
In scenarios where complex issues comprise multiple interconnected sub-problems, parent-child ticketing organizes them hierarchically.
This feature allows for systematic tracking and management of related issues, facilitating comprehensive resolution by addressing underlying dependencies and ensuring that all components of the problem are effectively addressed.
4. Ticket Prioritization
Prioritizing tickets involves categorizing incoming support tickets based on factors such as urgency, impact, or severity.
This enables support teams to allocate resources efficiently, ensuring that critical issues receive prompt attention while less pressing matters are managed appropriately. Effective ticket prioritization helps maintain service level agreements and enhances overall customer satisfaction.
5. Ticket Labels
Ticket labels are descriptive tags or categories assigned to tickets to facilitate organization, searchability, and filtering within the ticketing system.
By labeling tickets according to relevant attributes or characteristics, support teams can easily classify and group similar issues, streamlining management workflows and enabling quick retrieval of relevant information.
6. Internal Notes
Internal notes allow agents to communicate privately within the ticketing system, facilitating collaboration, knowledge sharing, and problem-solving among team members.
Agents can use internal notes to provide additional context, share insights, or coordinate actions without exposing sensitive information to customers, thereby enhancing efficiency and effectiveness in resolving issues.
7. Ticket Submission Forms
Ticket submission forms are standardized forms or templates that collect essential information from users when they report an issue or request assistance.
By structuring the information-gathering process, submission forms ensure completeness and accuracy in ticket creation, reducing the need for follow-up queries and expediting the resolution process.
6 Reasons Why Your Organization Needs a Ticketing System
A helpdesk ticketing system brings multiple capabilities and features to the table that can help you enhance the end-user experience. Here are some top ticketing system benefits you need to know:
1. Efficient Request Management
A ticketing system helps businesses manage incoming requests and issues from customers or employees in an organized and efficient manner. Right from a centralized help desk software inbox, you can capture requests from various channels – email, live chat, web forms, help center, and more.
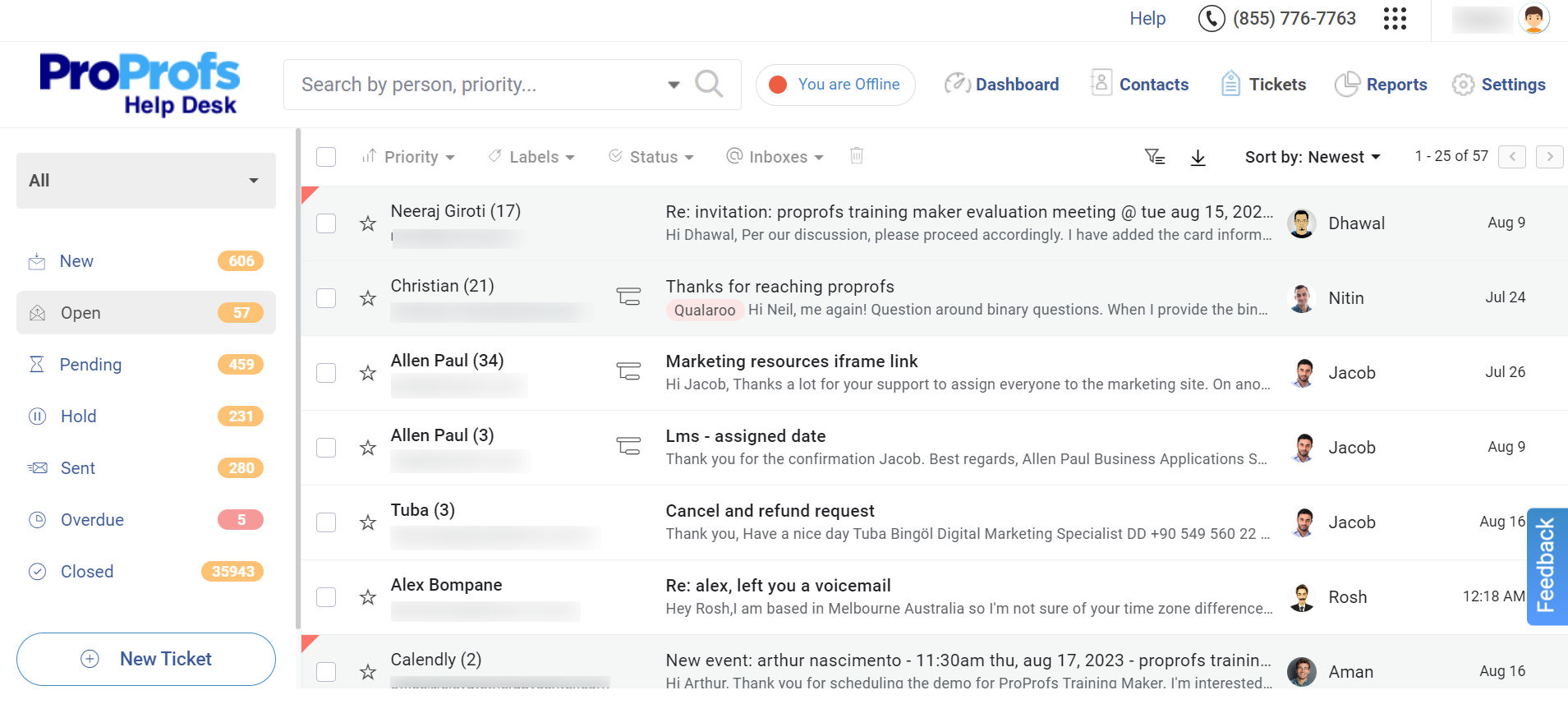
Each request is assigned a unique ticket number and can be tracked through its entire lifecycle, from creation to resolution. In addition, agents can get a 360-degree view of all ongoing issues along with their current statuses.
2. Improved Collaboration
A ticketing system allows multiple team members to collaborate on resolving a single ticket. This can help speed up the resolution process and ensure everyone is on the same page regarding the status of each request.
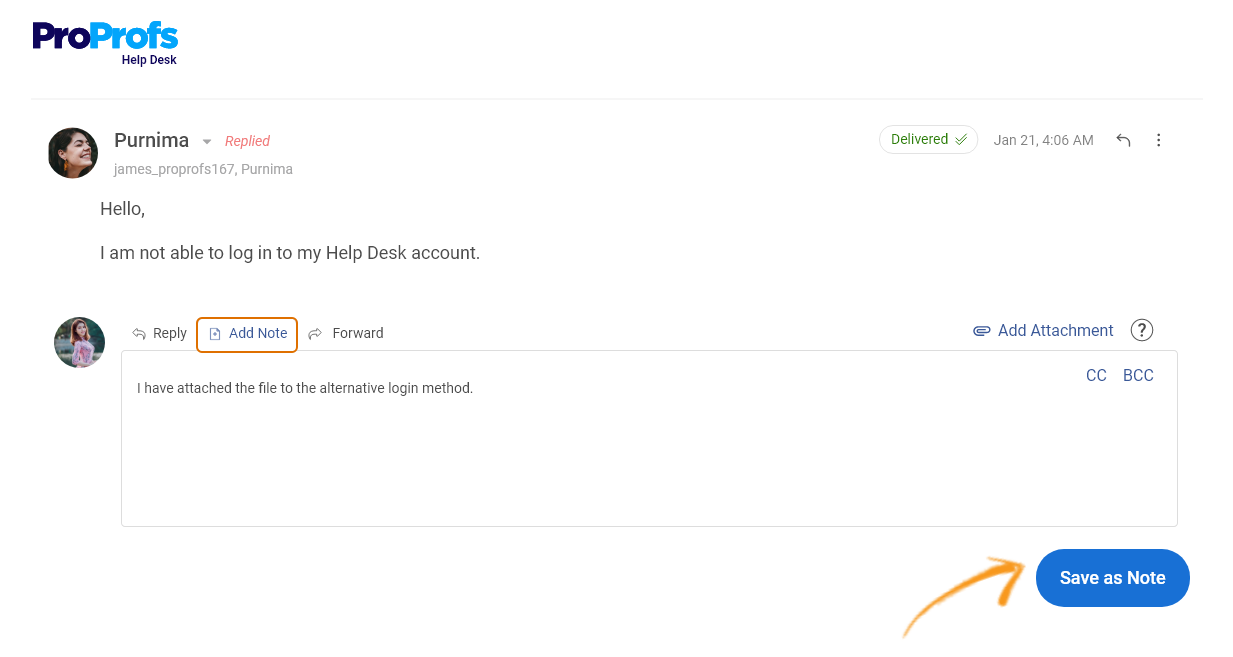
For example, agents can use internal notes to discuss complex issues together. They can even leave notes to share context or guide other agents who may work on the same issue in the future.
3. Enhance Customer Service
A ticketing system provides a centralized location for customer requests, making it easier for customer service agents to respond in a timely manner.
Customers also receive automatic notifications about the status of their requests, which can help reduce repeat inquiries and increase their confidence in the business. When every request and issue is taken care of at the right time, you can deliver memorable customer service experiences.
4. Track Performance Metrics
Another important benefit of ticketing systems is that they can provide your business with valuable performance metrics. From the reporting dashboard, you view all metrics in one place or add filters to view the metrics relevant to your purpose.
For instance, support managers can track KPIs and metrics such as response times, resolution times, ticket volume, and more. A careful analysis of reports can help you identify areas for improvement and optimize business processes.
5. Store Crucial Customer Data
A ticketing system provides a centralized location for storing and retrieving all communications related to internal and external services. For instance, you can easily access complaints registered by customers, or IT requests made by your internal employees.
Agents can refer to the ticket history to better understand the reason for present contact and personalize the entire experience. Moreover. this can help businesses maintain accurate records of customer interactions, which can be useful for compliance, audit, and legal purposes.
6. Capture User Feedback With Surveys
No matter how or when customers reach out to you for assistance, you must share surveys with them to monitor the service experience. For this reason, ticketing systems can be used to share automated surveys right after a ticket is marked as resolved or closed.
With the right feedback at your fingertips, you can identify areas for improvement, modify existing processes, and ensure that customers receive the best possible experience. You can even encourage customers to rate support agents on different parameters such as helpfulness, politeness, knowledge of the product, etc.
How Does a Ticket System Work? (With Example)
Here is a step-by-step explanation of how a support ticketing system works. To make it easier for you, each step is followed by an example.
Step 1: User Submits a Request
A user encounters a technical issue and submits a support request, either through a customer service portal, email ticketing system, live chat, form, or by calling the IT department. The request includes information such as the user’s name, contact information, and a description of the problem.
Example: John, an employee at a company, encounters an issue with his email account. He logs into the company’s IT support portal and submits a support request detailing the problem he’s experiencing, providing his name, email address, and a description of the issue.
Step 2: New Ticket Creation
The ticketing system automatically creates a new ticket, assigns it a unique number, and categorizes it based on the type of issue reported.
Example: The IT ticketing system automatically generates a new ticket for John’s email problem. The system assigns a unique ticket number to the request and categorizes it as an email-related issue.
Step 3: Ticket Assignment to IT Staff
The ticket is then automatically assigned to an appropriate agent based on their availability or skill sets. The agent receives an email notification of the new ticket and can view its details and any updates from the user through the ticketing system.
Example: The ticket is then automatically assigned to Sarah, a member of the IT support team known for her expertise in email systems. Sarah receives an email notification informing her of the new ticket and accesses the ticket details through the ticketing system.
Step 4: Resolution and Communication
The agent resolves the issue and updates the ticket with their progress. They can also communicate with the user through the ticketing system to gather additional information or provide updates.
Example: Sarah investigates John’s email issue, identifies the root cause, and begins working on a solution. She updates the ticket with her progress, noting any troubleshooting steps taken and requesting additional information from John if needed. Sarah also communicates with John through the ticketing system, providing him with updates on the status of his request and any actions taken to resolve the issue.
Step 5: Ticket Closure
Once the issue is resolved, the IT staff member marks the ticket as closed, and the user receives a notification that the issue has been resolved.
Example: After successfully resolving John’s email problem, Sarah marks the ticket as closed within the ticketing system. John receives a notification informing him that his issue has been resolved and that the ticket is now closed.
Step 6: End-User Feedback
But that’s not the end. A survey is automatically shared with the user that asks them to rate their service experience. You can use this feedback to gauge agent performance and measure user satisfaction.
Example: Following the resolution of his issue, John receives an automated survey asking him to rate his service experience with the IT support team. John provides feedback on the quality of service he received, allowing the company to gauge Sarah’s performance and measure John’s satisfaction with the support provided.
Improve Ticket Management With the Best Ticketing System
A ticketing system can help track every customer service ticket from start to finish. There is no need to worry about which issues were raised by which customer or when a request was registered by an internal employee.
A well-designed help desk ticketing system can streamline communication, automate processes, and improve response times. All these factors can together lead to increased operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
So if you have not yet decided which ticketing system to get for your business, we might have the perfect solution for you. ProProsf Help Desk combines the power of ticketing with a knowledge base, live chat, chatbots, reports, automation, and multiple other capabilities. Ready to embrace effortless ticket management and delight end-users?
Frequently Asked Questions
How can organizations measure the effectiveness of their ticketing system?
Organizations can measure the effectiveness of their ticketing system by tracking metrics such as resolution time, ticket backlog, customer satisfaction ratings, first-contact resolution rate, and agent performance. Analyzing these metrics provides insights into system efficiency, customer service quality, and areas for improvement to optimize support operations.
Read More: 10 Important Customer Satisfaction Metrics to Target in 2024
How can businesses select the right ticketing system for their needs?
Here are some tips to keep in mind while selecting a ticketing system:
- Identify specific requirements and objectives
- Evaluate the ease of use and customization options
- Consider scalability and flexibility
- Compare pricing models and total cost of ownership
- Seek user feedback and reviews
- Request demos or trials for hands-on evaluation
- Ensure compliance with security and regulatory standards
Can a ticketing system be customized to specific business needs?
Yes, ticketing systems can be customized to meet specific business needs through various means, such as configuring workflows, adding custom fields, integrating with other tools or systems, implementing automation rules, and branding interfaces. Customizing the system enhances efficiency, user experience, and alignment with organizational processes and objectives.